Figure 1.1 (p. 5)
Psy 330
Kantowitz Ch. 1
Overview of Psychological Research
I. A CLASS EXPERIMENT
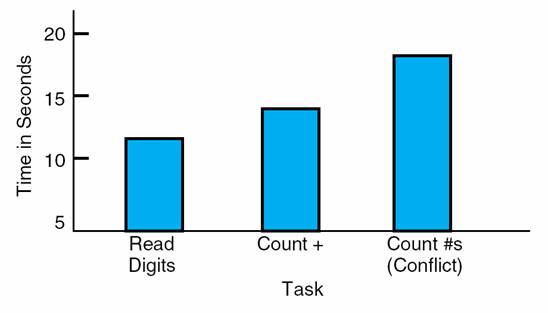
Reading & Counting--Are they rational, deliberate processes or are they automatic processes occurring with very little conscious effort?
Be able to address the following regarding this experiment:
Hypothesis:
Independent variable(s):
Dependent variable(s):
How many treatment groups? Name them.
Within-subjects or between-subjects design? Explain.
Regarding data analysis, what types of descriptive statistics should we use? inferential statistics?
What general conclusion can be made?

Figure 1.1
(p. 5)
II. MAKING SENSE OF THE WORLD
Conducting research--basic & applied
Evaluating research--must be a skilled critical thinker
What are the principles/characteristics of a good experiment?
Flawed research--confounding produces results with no internal validity
III. SOURCES OF KNOWLEDGE
Unscientific ways of knowing (methods of authority, tenacity, & a priori)
vs. Scientific way of knowing (a repeatable, self-correcting process that seeks to understand phenomena on the basis of empirical phenomena. Fixes belief on the basis of scientific method.
|
|
Non-Scientific (everyday) |
Scientific |
|
General
Approach
|
intuitive
|
empirical
|
|
Observation
|
casual,
uncontrolled
|
systematic,
controlled |
|
Reporting
|
biased,
subjective
|
unbiased,
objective
|
|
Concepts
|
ambiguous,
surplus meaning |
clear
definitions, operational specificity |
|
Instruments
|
inaccurate,
imprecise |
accurate,
precise
|
|
Measurement
|
not valid
or reliable |
valid and
reliable
|
|
Hypotheses
|
untestable
|
testable
(must be!)
|
|
Attitude
|
uncritical,
accepting |
critical,
skeptical
|
IV. THE NATURE OF THE SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION--public, empirical, self-correcting
What Is a Theory?
Induction and Deduction
From Theory to Hypothesis
Evaluating Theories--parsimonious? precise? testable? does it fit the data?
Intervening Variables--abstract concepts that link IVs to DVs
|