Psy 633
Sampling and Steps of Survey Research
G&F Ch.
5
I.
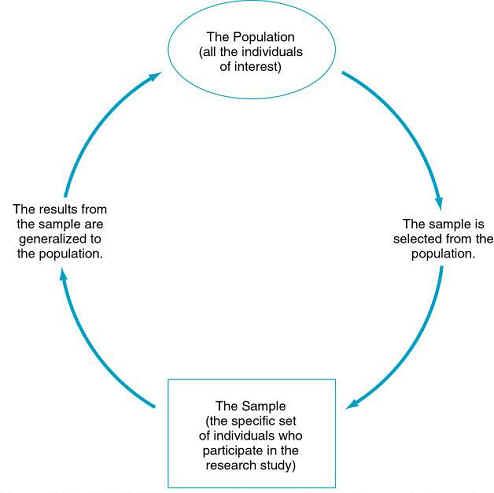
Population
vs. Sample
population
(target population) - all cases/individuals in which you are interested
sample - subset drawn from the population
element - each member of population
representativeness
– extent to which the sample exhibits the same characteristics as the
population
representative sample vs. biased sample
selection bias–when participants are selected in a way that increases the probability of obtaining a biased sample
The Relationship Between a Population and a Sample

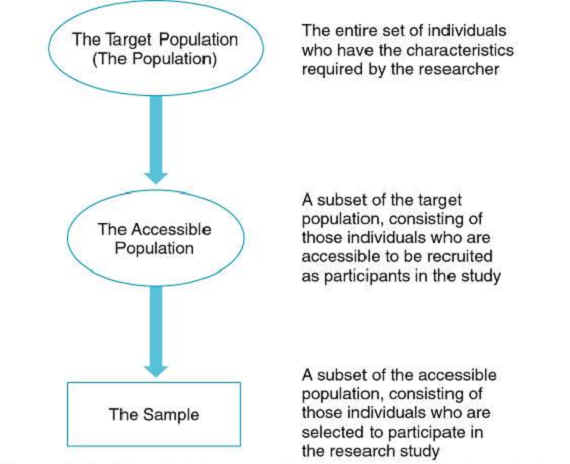
The Relationship Among the Target Population, the Accessible Population, and the Sample
II. Two Main Categories of Sampling Techniques (or methods)
A. Probability Sampling
The odds of selecting a particular element in a population are known and can be calculated.
Exact population size is known and all the elements or members are listed.
Each element of the population must have a specified probability of being selected.
Sampling frame - list all members of the population of interest
Researcher must use an unbiased selection process (random)
B. Non-probability sampling
The total size of the population is NOT known and each element can not be listed
Researcher uses a biased method of selection
What
is the risk of using non-probability sampling?
II. Specific Sampling Procedures
A. Probability Sampling Methods
1.
simple random sampling- every element has an equal and independent chance of being included
sampling with and without replacement--which is used more often?
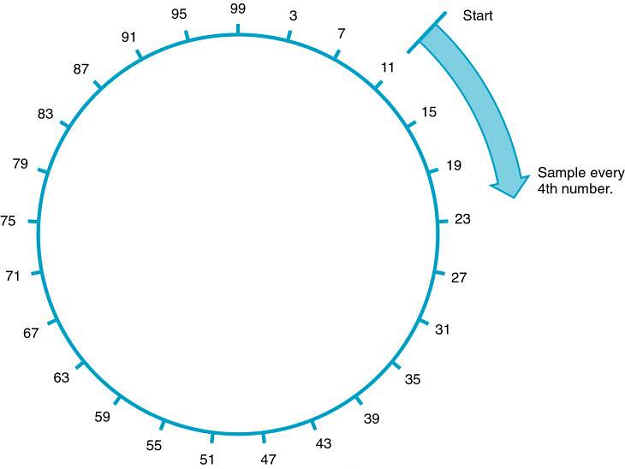
2. systematic sampling-selecting every nth participant after using simple random sampling to select the first participant
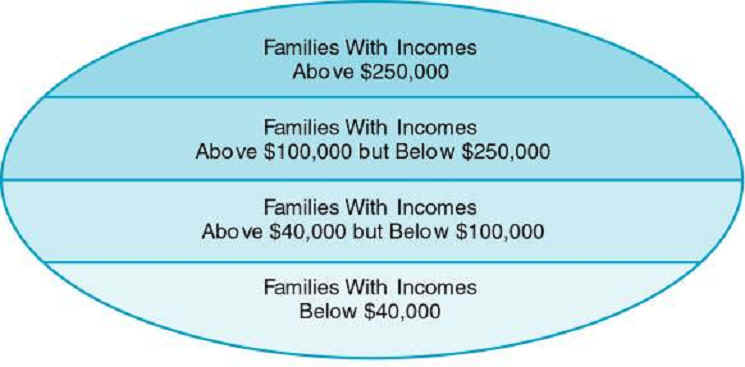
3. stratified random - identify specific subgroups (naturally occurring) and then select equal random samples from each of the subgroups.
4. proportionate stratified random sampling
5. Cluster Sampling--the individuals of a population already fall into groups, so the researcher randomly selects groups to participate instead of randomly selecting individuals
A Systematic Sampling Technique
Layers or Strata Defined by Annual Income
What are the advantages of probability sampling?
What are the disadvantages of probability sampling?
B. Non- Probability Sampling Methods
1. Convenience Sampling
Caution:
Typical research volunteers are different than non volunteers.
In what ways?
If convenience sampling is likely to lead to a biased sample, why do so many researchers use this method?
How do researchers compensate for the weaknesses of convenience sampling?
2. Quota Sampling
An attempt to make a convenience sample more representative.
Questions for Review:
Explain the difference between target and accessible populations.
What is the problem with a biased sample?
Explain the difference between probability and nonprobability sampling.
Explain how the generality of a study's results is affected by the sampling method used.
Name the sampling method used for these scenarios:
a. The State College is conducting a survey of student attitudes and opinions.
The plan is to use the list of all registered students and randomly select 50
freshmen, 50 sophomores, 50 juniors, and 50 seniors to make up the sample.
b. A second option for the college survey (see above) is based on the observation that the college accepts a large number of transfer students each year. As a result, the junior and senior classes were twice as large as the freshman and sophomore classes. To ensure that the sample reflects this difference in class size, the alternative plan is to determine the number of students in each class, then select a sample such that the number for each class in the sample is in direct relation to the number in each class for the entire college.
c. The County Democratic Committee would like to determine which issues are most important to registered Democrats in the county. Using the list of registered Democrats, the committee selects a random sample of 30 for telephone interviews.
d. A faculty member in the Psychology Department posts notices in classrooms and buildings on campus, asking for volunteers to participate in a human memory experiment. Interested students are asked to leave their names and telephone numbers.
e. An educational psychologist selects a sample of 40 third-grade children from two cooperating teachers at the local public school, ensuring that the sample is divided evenly with 20 boys and 20 girls.
STEPS IN SURVEY RESEARCH
·
Define the population of interest and determine the sampling procedure.
·
Define the research questions: What exactly do you want to know?
·
Will you administer the survey instrument using a written, questionnaire format
or an interview format?
·
How will you administer the survey (on-line, face-to-face, through the mail,
etc.)?
·
What type of questions are you going to use?
a. Open-ended: Respondents are asked to answer a question in their
own words.
E.g. "What is your opinion of your employer's affirmative action policies?"
b. Restricted: Closed-ended with a limited set of response alternatives.
A list of choices is given and they check the desired alternative.
E.g. "One of the major reasons for getting married is to have children."
Agree _________
Disagree_______
c. Rating Scales: Respondents circle a choice, a number on a scale,
or check a point on a line that best reflects their opinion.
E.g. "The US Congress should
increase spending on social programs."
Strongly disagree Don't know
Strongly agree
·
Make sure to avoid pitfalls in constructing questions, such as the following:
a. Double-barreled questions (that ask two different things).
E.g. "Do you believe there are equal opportunities for minorities and
women at your place of employment?
b. Loaded questions (that contain emotionally charged language).
E.g. " To what extent do you think the values of the Ku Klux Klan are alive and
well in the South?"
1
2
3
4
5
Not alive
uncertain
very much
Above question could be rephrased as:
"To what extent do you think support for racial segregation still exists in the
South?
1
2
3
4
5
very weak
uncertain
very strong
c. Leading questions (that bias people to respond in a given
way). E.g. "I agree with the
popular view that our current foreign policy is flawed."
better: "Our current foreign policy is flawed."
·
Ask important questions first: demographic information such as age, gender, or
household income should usually be obtained last.