1. Examples of negative externalities include pollution, barking dogs, and consumption of alcoholic beverages (many others are possible). Examples of positive externalities include restoring historic buildings, research into new technologies, and education (many others are possible).
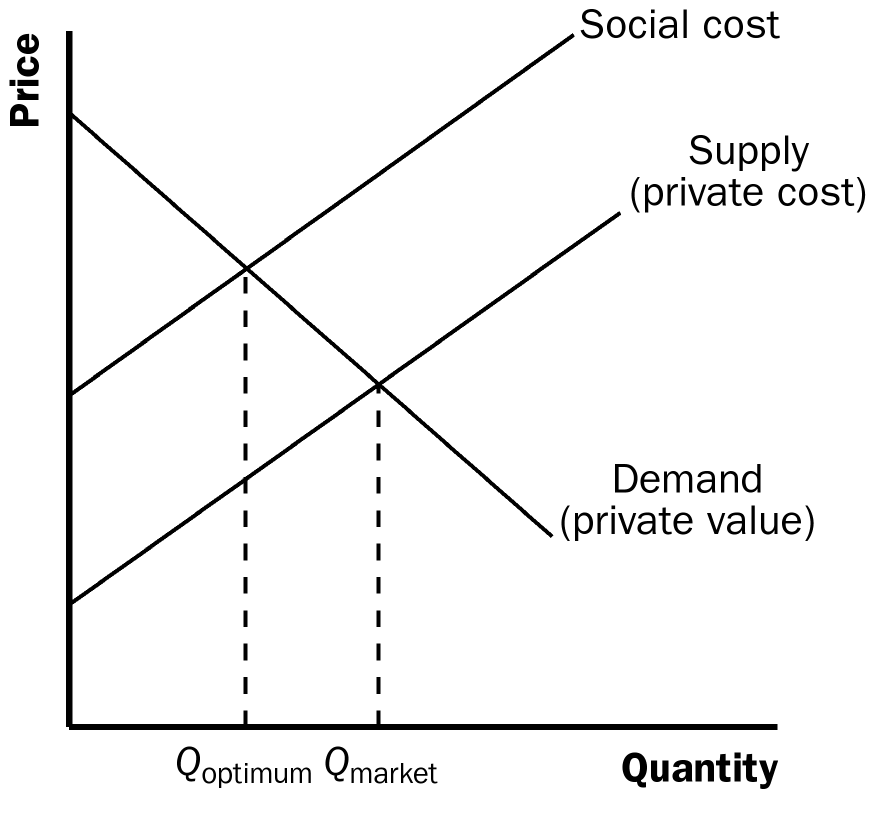
2. Figure 1 illustrates the effect of a negative externality. The equilibrium quantity provided by the market is Qmarket. Because of the externality, the social cost of production is greater than the private cost of production, so the social-cost curve is above the supply curve. The optimal quantity for society is Qoptimum. The private market produces too much of the good, as Qmarket is greater than Qoptimum.

Figure 1
3. The patent system helps society solve the externality problem from technology spillovers. By giving inventors exclusive use of their inventions for a period of time, the inventor can capture much of the economic benefit of the invention. In doing so, the patent system encourages research and technological advance, which benefits society through spillover effects.
1. The relationship between a firm's total revenue, profit, and total cost is profit equals total revenue minus total costs.
2. An accountant would not count the owner’s opportunity cost of alternative employment as an accounting cost. An example is given in the text in which Helen runs a cookie business, but she could instead work as a computer programmer. Because she's working in her cookie factory, she gives up the opportunity to earn $100 per hour as a computer programmer. The accountant ignores this opportunity cost because no money flow occurs. But the cost is relevant to Helen's decision to run the cookie factory.