1.
(a) Probability distribution
function for Y
|
Outcome |
Y
=
0 |
Y
=
1 |
Y
=
2 |
|
Probability |
0.25 |
0.50 |
0.25 |
(b)
Cumulative probability distribution function for
Y
|
Outcome |
Y
<
0 |
0
£
Y
<
1 |
1
£
Y
<
2 |
Y
³
2 |
|
Probability |
0 |
0.25 |
0.75 |
1.0 |
(c)
![]()
Using Key Concept
2.3:
![]() and
and
![]()
so that
![]()
2.
We know from Table 2.2 that
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() So
So
(a)
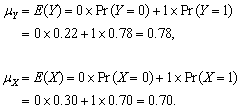
(b)

(c) Table 2.2
shows
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() So
So
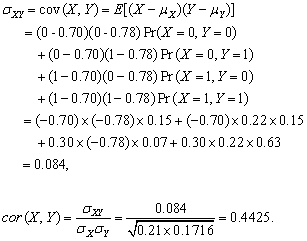
6.
The table shows that
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
(a)
![]()
(b)
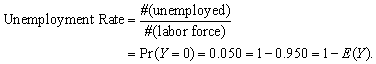
(c) Calculate the conditional probabilities first:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
The conditional expectations are
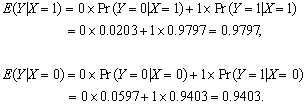
(d) Use the solution to part (b),
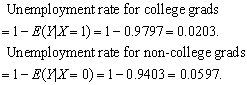
(e) The probability that a randomly selected worker who is reported being unemployed is a college graduate is
![]()
The probability that this worker is a non-college graduate is
![]()
(f) Educational achievement and employment status are not independent because they do not satisfy that, for all values of x and y,
![]()
For example,
![]()
10.
Using the fact that if
![]() then
then
![]() and Appendix Table 1,
we have
and Appendix Table 1,
we have
(a)
![]()
(b)
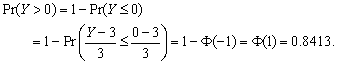
(c)
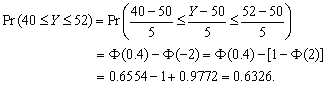
(d)
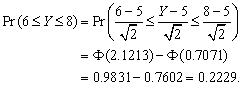
12. (a) 0.05
(b) 0.950
(c) 0.953
(d) The tdf distribution and N(0, 1) are approximately the same when df is large.
(e) 0.10
(f) 0.01