Laboratory Activities:
You will be working in groups on most lab activities. Your log book (lab book or lab journal) does not have to be "neat" but it must be organized. Make sure to put all pertinent information in your log book. Staple or tape graphs or data that you have printed so that they do not fall out. If you do not know how a particular piece of apparatus works read a Lab Equipment Manual or ask [other groups are great resources too!]. Summaries are graded on a 4 point scale (see the general lab rubric) and are due on Tuesdays but may be submitted early so you have time to correct. for prior weeks at the st
VPython |
|
To run a Python program you will need to opentheVIDLE program which is a GUI (graphical user interface) for Python. |
|
Date |
#
|
Lab Activities
|
Simulations from PhET | |
Tuesday Jan. 15 |
1
|
Investige Coulomb's Law. Use the simulator to learn how to control the charged puck using the Electric field |
Electric Field Hockey |
|
Tuesday Jan. 22 |
2
|
|
 Balloons and Static Electricity |
 John Travoltage |
Tuesday Jan. 29 |
3
|
Investige electric fields. Explore charge distributions and the resulting electric fields as well as the forces on the charged objects. Use the simulators to learn how to control a charged object. |

Electric Field Hockey |
Electric Field of Dreams |
Thursday Feb. 5 |
|
Lab Combine #1 Electric Fields: A more realistic model for the force on the repulsive force on a charged sphere from a plate. |
||
Tuesday Feb. 12 |
4
|
Investigate voltage (aka potential difference). Use the simulator to determine the relationship between electric fields and voltage. |
Charges and Fields |
|
Tuesday Feb. 19 |
5
|
Explore both permanent magnets and electromagnets. Use both the compass and meter to describe the magnetic field.
Bonus: Explore the interaction between electric fields and magnetic fields using the electromagnetic lab. |
 Magnets and Electromagnets |
 Electromagnetic Lab |
Tuesday Feb. 26 |
6
|
Investigate Ohm's observation. Use the simulator to investigate current flow and voltage in a circuit. For a constant voltage how does the resistance change the current in a circuit. |
 Circuit Construction (DC) |
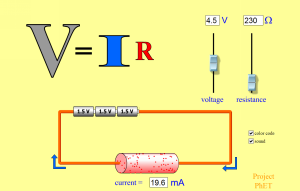 Ohm's Observation |
Tuesday
March 5 |
|
Lab Combine #2
Magnetic Fields: You will be constructing an electromagnet as well as modeling the magnetic field produced by a loop of wire.
|
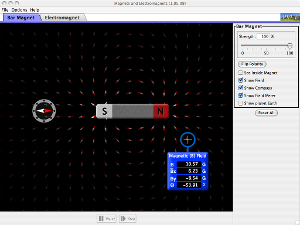
Electromagnets |
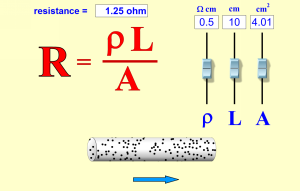 Resistance in a Wire Resistance in a Wire |
Tuesday March 19 |
7
|
Use the simulator to investigate current and voltage as a function of time in a circuit. Determine the RC time constant for a circuit. |
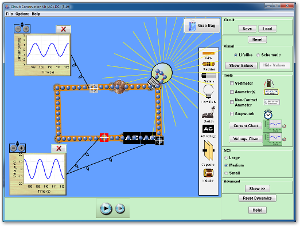
Circuit Construction |
Capacitor Lab |
Tuesday
March 26 |
8
|
Use the circuit simulator to explore more complex DC circuits. Investigate the difference between resistors in series and in parallel. Explore max power in a circuit. |

Circuit Construction (AC & DC) |
 Resistance in a Wire Resistance in a Wire |
Tuesday April 2 |
9
|
Determine the size of atoms by looking at the spectra (wavelength of light emitted).
Note: If needed, read the Ocean Optics Spectromete experimental tutorial. Feel free to consult external references on spectral lines.
|
 Models of the Hydrogen Atom |
|
Tuesday April 9 |
10
|
Create a model of a protron inside a cyclotron.
The motion of a charged particle in a magnetic field is a basic phenomena. The Hall effect is a direct consequence of this phenomena.
Use the simulation to visualize the effect of a moving charged object. |
 Radiating Charge |
|
Tuesday April 15 |
|
Student Academic Conference | Attend 3 physics presentations and turn in summaries for lab credit. | |
Thursday April 15 |
|
Lab Combine #3
Use the simulator to determine how to induce a voltage in the circuit and light the bulb.
Make a simple speaker or make a simple motor
|
 Electromagnetic Lab |
 Faraday's Law |
Thursday April
23 |
11
|
Useful
demos: |
Bending Light |
 Radio Waves and Electromagnetic Fields |
Thursday April 30 |
12
|
Determine the focal length simple lenses and use them to consruct a telescope. Useful demos: Converging Lens, Diverging Lens, Diverging Mirror
Feel free to consult external references on illumination . |
Geometric Optics |
 Color Vision |
AUX
|
You need AC voltage to appreciate how an LCR circuit can resemble a simple harmonic oscillator.
Useful Oscilloscope and Function Generator knobs . |

Circuit Construction (AC & DC) |
||
| C-level: Conceptual
diagram and summary due on lab day. Students must receive a 3 (out of 4) on
the C-level to move on to the B-Level. B-level: Basic lab must be checked on lab day for A-level work to earn credit. Edited lab summaries are due by the following Tuesday (best to get feedback on lab day). Students must receive a 2 (out of 4) on the B-Level to move on to the A-level. A-level: Advanced lab summaries due by following Tuesday. |
| Labs are evaluated via a general rubric for each level with scores of 0=not present, 1=poor, 2=needs improvement, 3=meets expectations and 4=exceeds expectations. |
| Your percent lab grade is given by %=(5*C + 3*B + 2*A + 42)/82*100%. You may find it easier to look at a table of scores. |
