|

|
English Structures
Writing Systems
|
Introducing Image-Based Writing Systems
Read the sentences below:
http://www.bethanyroberts.com/RebusValentines.htm |
These sentences should not be hard for native speakers of English to read. There is,
however, a trick to reading them.
- The meaning comes from a combination of picture and sound.
- The pictures represent a real world object that has a corresponding
word.
- The word has a pronunciation that suggests another set of sounds
with a different meaning.
So, with this combination of images and letters, the sentences are easy
to read if you read out loud: it's really the pronunciation that matters, not the pictures. |
| What you just read was a rebus. In a rebus puzzle, the pictures no longer
have a visual relationship to their meanings, only a phonetic relationship. The pictures have become phonographic symbols. |
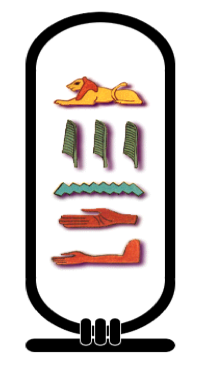
| Now consider this image: |
|
|
Ancient Egyptian used a writing system similar to the rebus system.
- The carvings (glyphs) stood for the entire words of the things
they depicted. for example, a picture of a lion stood for the whole word lion.
- The carvings could also stand for individual sound segments or combinations of sound segments. For example, if we were reading hieroglyphs with English words, the carving of a lion could stand for either the whole word lion or for the sound that begins the word lion, [ l ], If it stabds for the sound, it must combine with other carvings to spell out all the sounds of another word, as the glyphs in the example to the left do.
|
Mouse over the translation chart link to read these hieroglyphics. By the way hiero means sacred or holy, and glyph means "carving", so hieroglyphic means "sacred
carvings." The name was coined by early archeologists because the
hieroglyphs they initially found were carved into temples.
For more
information. |
|
The Ancient Egyptian system is not as simple as the pictures in the rebus samples
above. This system is also not the same as the one English uses.
How is the English writing system different from Egyptian hieroglyphics?
And how many different ways of writing do you suppose there are? |
| Go to Part 3 |
|
American Sign Language The sign language used by the deaf community in the United States.
Test of English for International Communication. A standardized exam for Educational Testing Services that is intended to determine the general capability of an NNSE to use English to conduct business. It is used by some businesses, predominantly in Asia, in hiring.
Test of English as a Foreign Language. A standardized exam from Educational Testing Services that is intended to determine the general capability of an NNSE to use English as the language of insruction .It is used as an admissions requirement by most US universities and colleges for international students.
Teaching English to Speakers of Other Languages. A term that encompasses both TEFL and TESL. It is the name of the professional organization to which many teachers belong. TESOL the organization has many regional affiliates both in the US and abroad.
Teaching English as Second Language. Refers to the activity of teaching the English language as a tool necessary for some daily task like instruction, shopping, or interpersonal interactions.
Teaching English as a Foreign Language. Refers to the activity of teaching the English language as an intellectual, academic pursuit to non-native speakers of English.
Native Speaker of English. Refers to a person who acquired English in infancy and young childhood as a first language.
Native Speaker. Refers to a person whose relationship to a language is that it was encountered in infancy and young childhood as the dominant language of the environment.
Non-Native Speaker of English. Refers to a person who didn't acquire English as a first language, but came to it after another language was established.
Non-Native Speaker. Refers to a person whose relationship to a particular language is that he/she didn't encounter it while initially acquiring language, but came to it after another language was established.
Limited English Proficient. An adjectival phrase used to refer to the same students as ELL refers to. LEP is falling into disuse as it focuses attention on student deficiency rather than on the positive attribute of learning. Is being replaced by ELL.
Second Language. Refers to any language gained subsequent to the first or native language. It is acquired or learned secondarily to the native language. Doesn't refer to the ordinal numbering of languages, only to the relationship of a particular language to a persons native language.
First Language. Refers to the language that an individual encounters as an infant and young child; a persons native language.
English for Specific Purposes. Refers to the goal of learning English to use it for highly focused activity, such as for business or for aviation communication.
English as a Second Language Program. refers to a school program that is purposefully structured to provide instruction on the English language to NNSEs. An ESL program does not typically include instruction in any other subjects than English. An ESL program may be a component of a larger ELL program at a school.
English as a Second Language. Refers to the subject matter of the English language and the methodology for teaching the English language to non-native speakers. ESL makes no reference to the subjects other than English, but it is not methodology alone either, it refers to teaching the English language as content area. Typically, ESL refers to the study of English in a country where it is used for at least one daily task, such as instruction, interpersonal relations, or shopping.
English Langauge Learner Program. Refers to a school program that is purposly structured to provide instruction on the English language and instruction in other content areas to English Language Learners.
English Language Learner. Refers to students who are in the process of learning English, whether they are in ESL classes exclusively or a combination of ESL classes and other subject area classes.
English as a Foreign Langauge. Refers to the study of English as an intellectual, academic pursuit, not a a language whose use is necessary or desirable for daily life, although it may be used as a research tool. Typically, EFL is the study of English in a country where English is not a language of instruction or daily interactions, such as in Italy or in Saudi Arabia.
English for Academic Purposes. Refers to the goal of learning English to use it as the language of instruction for other subject areas.
Refers to a school program that is purposely structured so that students will use two languages on a daily basis.
Refers to the use of two languages in any capacity on a daily basis. A bilingual person uses two languages on a daily basis--for work and at home, perhaps, or for different subjects at school. Can also refer to the ability to use two languages, even if not used daily.