So far, we have only dealt with whole numbers that are used to count how many items are in a group of items. (That is, we have been using the cardinal number of a set.) These numbers were called whole numbers because they count whole things.
In order to extend our idea of number to include parts of wholes, we use fractions such as halves, thirds, and fifths.
Fraction (mathematics) - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Common Fractions: Common fractions are written in the form 
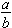 , where a, b are whole numbers and b
, where a, b are whole numbers and b
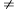 0. The top numeral,a, is called the numerator and the bottom numeral, b, is called the denominator.
0. The top numeral,a, is called the numerator and the bottom numeral, b, is called the denominator.
Note. The most proper way to write a fraction is in the vertical format, 
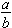 . The slanted format, a/b, is for writing fractions in a typed sentence. Many students who learn to write fractions only in the slanted form have problems interpreting mixed numbers and working with rational expressions in algebra. For these reasons, your instructor may require that all fractions in this course be written in the vertical form.
. The slanted format, a/b, is for writing fractions in a typed sentence. Many students who learn to write fractions only in the slanted form have problems interpreting mixed numbers and working with rational expressions in algebra. For these reasons, your instructor may require that all fractions in this course be written in the vertical form.
Further Note. In general, the numerators and denominators of fractions may be values other than whole numbers. For example, later in this course we will need to write some fractions using integers and some fractions with decimals that are not simplified. Also, a decimal is an abbreviation of a common fraction that has a denominator that is an exponential power of ten. For simplicity, we use the term fraction even when we are talking about common fractions.
Common Fractions: 
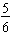 and
and 
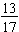
Decimal Fractions: 0.7 and 0.379 since they are the common fractions 
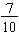 and
and 
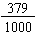
Algebraic Fractions: 
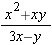 and
and 
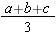
Some Other Fractions: 
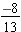 and
and 
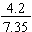
A basic way to interpret a fraction (common fraction) is by dividing a whole object into several equal parts. The denominator tells how many equal parts the whole is subdivided into. The numerator tells the number of those parts that are under consideration.
Example:
If is one whole, then the shaded portion of
is

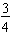 of the whole. In this example, the 3 is the numerator describing the shaded part and the 4 is the denominator telling how many equal parts the whole has been divided into.
of the whole. In this example, the 3 is the numerator describing the shaded part and the 4 is the denominator telling how many equal parts the whole has been divided into.
Examples: Here are several different models for the fraction 
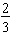 .
.
Discrete model
Two-thirds of the set are shaded circles.
Number line model
The vector is two-thirds of a unit.
Area model
Two-thirds of the rectangle is shaded.
Volume model
Two-thirds of the cylinder is shaded.
return to top | previous page | next page